Broadband T-shaped microstrip-fed U-slot coupled patch antenna Jang, Y. Publication: Electronics Letters. Pub Date: 2002 DOI: 10.1049/el:20020364. By loading the metasurface on the microstrip slot antenna, linearly polarized (LP) waves from the source antenna are converted into circularly polarized (CP) waves. Then, by etching three more parasitic square cross gaps in the middle of the metasurface, enhanced impedance bandwidth and axial ratio bandwidth (ARBW) are achieved. We propose a miniaturized wideband metasurface antenna for 60-GHz antenna-in-package applications. With the glass integrated passive device manufacturing technology, we introduce a coplanar-waveguide-fed (CPW-fed) ring resonator to characterize the material properties of the glass substrate. The proposed antenna is designed on a high dielectric constant glass substrate to achieve antenna. A dual-band microstrip patch antenna (MPA) based on a polarization conversion metasurface structure was designed. By etching the complementary split ring resonator (CSRR) on the ground plane, a new resonance frequency is generated. The proposed antenna is obtained through optimizing the structural parameters of CSRR. Compared with the antenna without CSRR, the return loss of the proposed.
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Ham Radio
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Antenna
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Long Range
- Mu-near-zero Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antenna
- Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas For Sale

Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Ham Radio
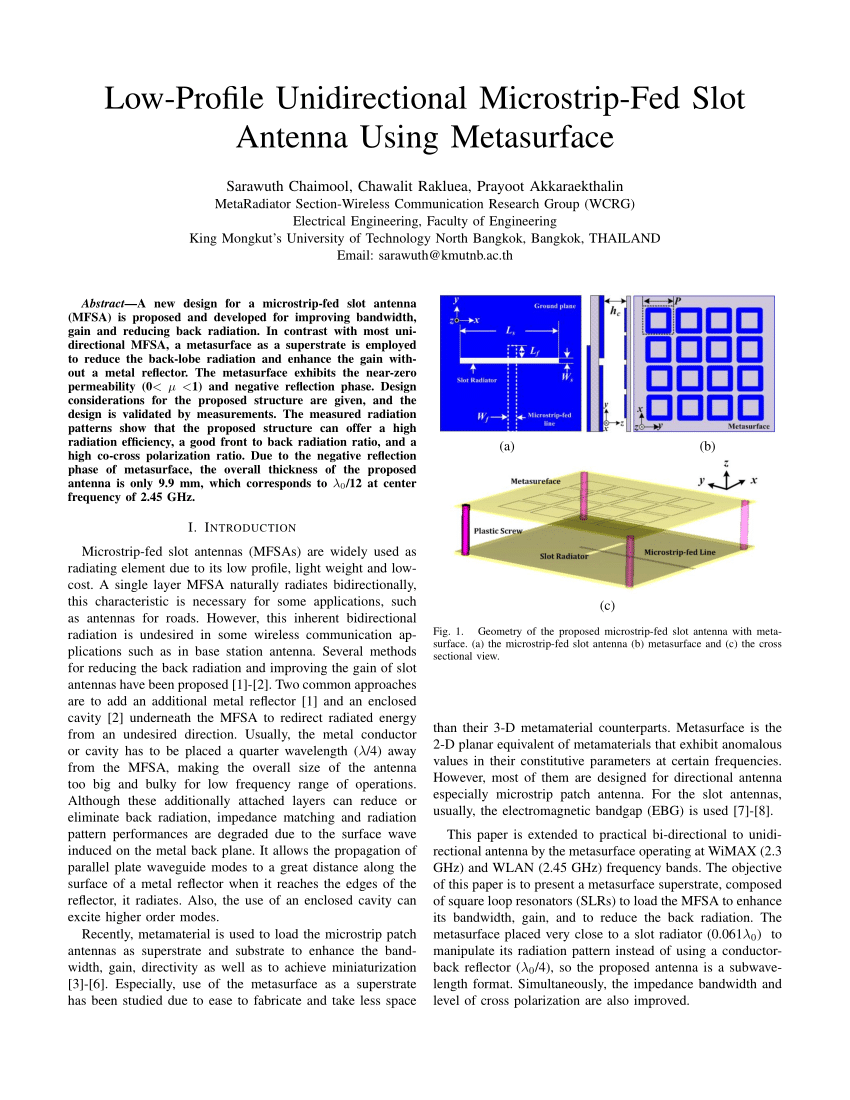
Abstract
The metasurface concept has emerged as an advantageous reconfigurable antenna architecture for beam forming and wave-front shaping, with applications that include satellite and terrestrial communications, radar, imaging, and wireless power transfer. The metasurface antenna consists of an array of metamaterial elements distributed over an electrically large structure, each subwavelength in dimension and with subwavelength separation between elements. In the antenna configuration we consider, the metasurface is excited by the fields from an attached waveguide. Each metamaterial element can be modeled as a polarizable dipole that couples the waveguide mode to radiation modes. Distinct from the phased array and electronically-scanned-antenna architectures, a dynamic metasurface antenna does not require active phase shifters and amplifiers but rather achieves reconfigurability by shifting the resonance frequency of each individual metamaterial element. We derive the basic properties of a one-dimensional waveguide-fed metasurface antenna in the approximation in which the metamaterial elements do not perturb the waveguide mode and are noninteracting. We derive analytical approximations for the array factors of the one-dimensional antenna, including the effective polarizabilities needed for amplitude-only, phase-only, and binary constraints. Using full-wave numerical simulations, we confirm the analysis, modeling waveguides with slots or complementary metamaterial elements patterned into one of the surfaces.
 7 More
7 More
Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Antenna
- Received 27 June 2017
Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas Long Range
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.8.054048
Mu-near-zero Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antenna
© 2017 American Physical Society
Metasurface For Microstrip-fed Slot Antennas For Sale
Physics Subject Headings (PhySH)
